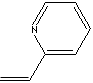
| 2-VINYLPYRIDINE | ||
|
PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION |
||
| CAS NO. | 100-69-6 |
|
| EINECS NO. | 202-879-8 | |
| FORMULA | (CH2=CH)C5H4N | |
| MOL WT. | 105.14 | |
|
H.S. CODE |
2933.39 | |
| TOXICITY |
|
|
| SYNONYMS | 2-Ethenyl-pyridine; alpha-Vinylpyridine; 2-Vinylypyridine; | |
| DERIVATION |
|
|
|
CLASSIFICATION |
|
|
|
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES |
||
| PHYSICAL STATE |
clear liquid |
|
| MELTING POINT |
-50 C |
|
| BOILING POINT | 158 - 160 C | |
| SPECIFIC GRAVITY | 0.97 - 0.98 | |
| SOLUBILITY IN WATER | 27 (g/l) | |
| SOLVENT SOLUBILITY | soluble in dilute acids, alcohol, hydrocarbons, esters, ketones. | |
| pH | 8 | |
| VAPOR DENSITY | ||
|
AUTOIGNITION |
|
|
|
NFPA RATINGS |
Health: 2; Flammability: 2; Reactivity: 2 | |
|
REFRACTIVE INDEX |
1.5495 | |
| FLASH POINT | 51 C | |
| STABILITY | Reactive. Inhibitor prevents polymerization. | |
|
APPLICATIONS |
||
| Vinyl: the univalent chemical radical H2C=CHCl-, derived from ethylene. It is a
highly reactive, easily polymerizing, and low cost monomer used as basic
materials for one of largest-selling plastic. In addition to its application of
polymerization to make plastics with huge amount, vinly is applied in flavor and
fragrance manufacturing. This radical is also useful in biochemistry study such
as protein sequencing and enzyme inhibiting.
Vinylypyridines are co-monomer in styrene-butadiene polymers to promote adhesion between the rubber compound and supporting fibers (or cords) in tires, belts, hoses. Intermediate for manufacturing chemical compounds. They are also used in manufacturing pharmaceuticals and bio-compounds. |
||
| SALES SPECIFICATION | ||
|
APPEARANCE |
clear liquid |
|
|
ASSAY |
98.0% min |
|
|
WATER |
0.2% max |
|
|
INHIBITOR |
0.1% max (4-tert-butylcatechol) |
|
|
TRANSPORTATION |
||
| PACKING | 200kgs in drum | |
| HAZARD CLASS | 6.1 (Packing Group: II) | |
| UN NO. |
3073 |
|
| OTHER INFORMATION | ||
| Hazard Symbols: XN, Risk Phrases: 10-20/21-25-34, Safety Phrases: 26-36/37/39-45 | ||
| GENERAL DESCRIPTION OF PYRIDINE | ||
|
PYRIDINE,
also called azabenzene and azine, is a heterocyclic
aromatic tertiary amine characterized by a six-membered
ring structure composed of five carbon atoms and
a nitrogen which replace one carbon-hydrogen unit
in the benzene ring (C5H5N). The simplest member of the
pyridine family is pyridine itself. It is colorless,
flammable, toxic liquid with a unpleasant odor,
miscible with water and with most organic solvents,
boils
at 115 C. Its aqueous solution is slightly alkaline. Its conjugate acid is called
pyridinium cation, C5H5NH+,
used as a oxidation agent for organic synthesis..
Pyridine is a base with
chemical properties similar to tertiary amines. Nitrogen in the ring system
has an equatorial lone pair of electrons, that does not
participate in the aromatic pi-bond. Its
aqueous solution is slightly alkaline. It is incompatible
and reactive with strong oxidizers and strong acids,
and reacts violently with chlorosulfonic acid, maleic
anhydride, oleum, perchromates, b-propiolactone,
formamide, chromium trioxide, and sulfuric acid.
Liquid pyridine easily evaporates into the air.
If it is released to the air, it may take several
months to years until it breaks down into other
compounds. Usually,
pyridine is derived from coal tar or synthesized
from
other chemicals, mainly acetaldehyde and ammonia. Pyridine compounds
are found in nature. For example, nicotine
from tobacco, ricinine from castor bean, pyridoxine or vitamin B and P products, alkaloids
(such as coniine, piperine and nicotine), and etc.
Some pyridine compounds consumed largely are;
Picoline :
Three structural isomers of methyl pyridines (alpha, beta, gamma-
positions) Pyridine and its derivatives are very important in industrial field as well as in bio chemistry. Nucleotide consist of either a nitrogenous heterocyclic base (purine or pyrimidine). Three major pyrimidines in living systems are cytosine, thymine, and uracil. Pyrimidine and its derivatives are biologically important components of nucleic acids (DNA, RNA) and coenzymes. Some pyridine system is active in the metabolism in the body. They can be the parent compound of many drugs, including the barbiturates. Pyridine and its derivatives are used as solvents and starting material for the synthesis of target compounds such as insecticides, herbicides, medicines, vitamins, food flavorings, feed additives, dyes, rubber chemicals, explosives, disinfectants, and adhesives. Pyridine is also used as a denaturant for antifreeze mixtures, as a dyeing assistant in textiles and in fungicides. Compounds not made from pyridine but containing its ring structure include niacin and pyridoxal; isoniazid, nicotine, and several other nitrogenous plant products. |
||